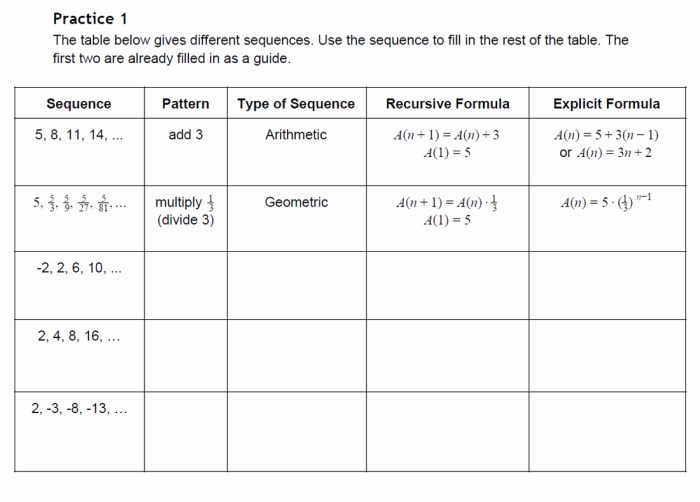
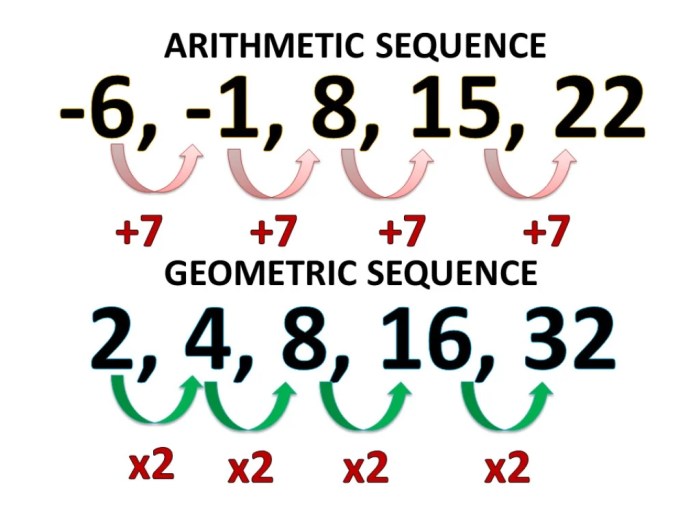
In the realm of mathematics, change plays a pivotal role in understanding the behavior of sequences. Among the various types of sequences, arithmetic and geometric sequences stand out for their unique properties and applications. This discussion delves into the concept of change in arithmetic and geometric sequences, exploring their definitions, formulas, and key differences.
Change in Arithmetic and Geometric Sequences
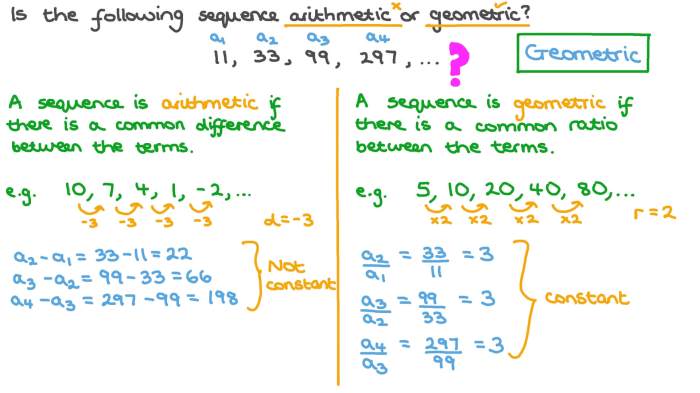
Sequences are ordered lists of numbers that follow a specific pattern. Arithmetic and geometric sequences are two common types of sequences that exhibit different patterns of change.
1. Arithmetic Sequences, Change in arithmetic and geometric sequences
An arithmetic sequence is a sequence in which the difference between any two consecutive terms is constant. The constant difference is called the common difference, denoted by d.
- Example:The sequence 3, 7, 11, 15, 19 is an arithmetic sequence with a common difference of 4.
- Formula for nth term:The nth term of an arithmetic sequence is given by the formula an= a 1+ (n – 1)d , where a1is the first term and nis the term number.
2. Geometric Sequences
A geometric sequence is a sequence in which the ratio of any two consecutive terms is constant. The constant ratio is called the common ratio, denoted by r.
- Example:The sequence 2, 6, 18, 54, 162 is a geometric sequence with a common ratio of 3.
- Formula for nth term:The nth term of a geometric sequence is given by the formula an= a 1– r (n- 1) , where a1is the first term and nis the term number.
3. Change in Arithmetic Sequences
The change in an arithmetic sequence is the common difference, d. It represents the amount by which each term increases or decreases compared to the previous term.
- How to find the change:To find the change in an arithmetic sequence, subtract any two consecutive terms. The result will be the common difference.
- Example:In the arithmetic sequence 3, 7, 11, 15, 19, the change is 4 because 7 – 3 = 11 – 7 = 15 – 11 = 19 – 15 = 4.
4. Change in Geometric Sequences
The change in a geometric sequence is the common ratio, r. It represents the factor by which each term increases or decreases compared to the previous term.
- How to find the change:To find the change in a geometric sequence, divide any two consecutive terms. The result will be the common ratio.
- Example:In the geometric sequence 2, 6, 18, 54, 162, the change is 3 because 6 ÷ 2 = 18 ÷ 6 = 54 ÷ 18 = 162 ÷ 54 = 3.
5. Comparing the Change in Arithmetic and Geometric Sequences
The change in an arithmetic sequence is constant, while the change in a geometric sequence is a factor. This means that the terms of an arithmetic sequence increase or decrease by a fixed amount, while the terms of a geometric sequence increase or decrease by a constant factor.
- Example:In the arithmetic sequence 3, 7, 11, 15, 19, the change is 4. Each term increases by 4 compared to the previous term.
- Example:In the geometric sequence 2, 6, 18, 54, 162, the change is 3. Each term is multiplied by 3 to get the next term.
FAQ Section
What is the difference between an arithmetic sequence and a geometric sequence?
In an arithmetic sequence, the difference between any two consecutive terms is constant, while in a geometric sequence, the ratio between any two consecutive terms is constant.
How do you find the change in an arithmetic sequence?
The change in an arithmetic sequence is equal to the difference between any two consecutive terms.
How do you find the change in a geometric sequence?
The change in a geometric sequence is equal to the ratio between any two consecutive terms.