Unlike factitious disorders psychophysiological disorders – Unlike factitious disorders, psychophysiological disorders are characterized by genuine physical symptoms that are triggered or exacerbated by psychological factors. This distinction is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment, highlighting the need for a nuanced understanding of the interplay between mind and body.
Delving into the complexities of these disorders, we will explore their definitions, etiologies, clinical presentations, and treatment approaches. By unraveling the intricate tapestry of psychophysiological disorders, we gain insights into the profound impact of psychological distress on physical well-being.
Definition and Key Characteristics: Unlike Factitious Disorders Psychophysiological Disorders
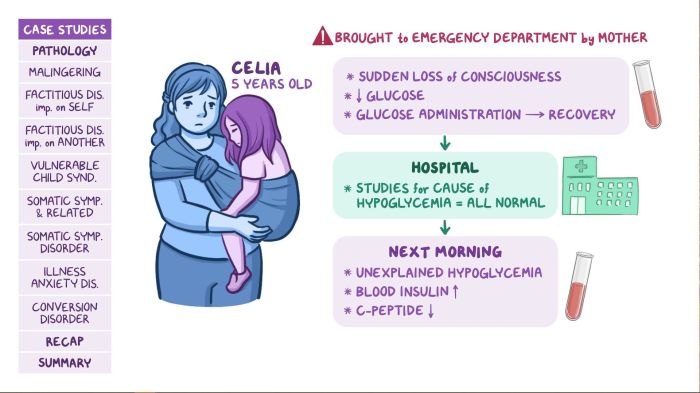
Factitious disorders and psychophysiological disorders are both conditions that involve physical or psychological symptoms that are intentionally produced or exaggerated by the individual.
Factitious disordersare characterized by the deliberate production or exaggeration of physical or psychological symptoms for the purpose of assuming the sick role. Individuals with factitious disorders may present with a wide range of symptoms, including physical pain, fatigue, neurological problems, and psychiatric symptoms.
The motivation for producing or exaggerating these symptoms is typically to gain attention, sympathy, or care from others.
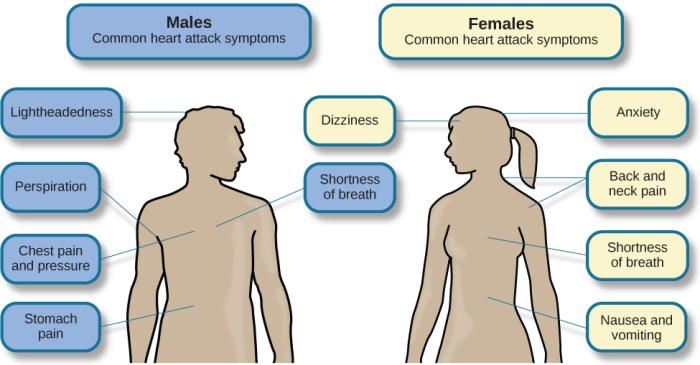
Psychophysiological disorders, on the other hand, are characterized by the presence of physical symptoms that are caused or exacerbated by psychological factors. Individuals with psychophysiological disorders may experience symptoms such as headaches, gastrointestinal problems, or cardiovascular problems. The psychological factors that contribute to the development of psychophysiological disorders may include stress, anxiety, or depression.
| Characteristic | Factitious Disorders | Psychophysiological Disorders |
|---|---|---|
| Symptoms | Intentionally produced or exaggerated physical or psychological symptoms | Physical symptoms caused or exacerbated by psychological factors |
| Motivation | Gaining attention, sympathy, or care | Coping with stress, anxiety, or depression |
| Diagnostic Criteria | DSM-5 criteria: Intentional production or exaggeration of symptoms; absence of external rewards; evidence of psychological distress or impairment | DSM-5 criteria: Physical symptoms caused or exacerbated by psychological factors; evidence of psychological distress or impairment |
FAQ Overview
What are the key differences between factitious disorders and psychophysiological disorders?
Factitious disorders involve intentionally feigning or producing physical or psychological symptoms for external rewards, while psychophysiological disorders involve genuine physical symptoms triggered or exacerbated by psychological factors.
How are psychophysiological disorders diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a thorough medical evaluation to rule out underlying medical conditions, followed by a psychological assessment to identify the psychological factors contributing to the symptoms.
What are the common treatment approaches for psychophysiological disorders?
Treatment typically involves a combination of psychotherapy, medication, and lifestyle modifications aimed at addressing the underlying psychological factors and managing the physical symptoms.