Delve into the fascinating world of gas exchange with Bioflix activity: gas exchange — inhaling and exhaling. This activity provides an immersive exploration of the fundamental processes that sustain life, shedding light on the intricate mechanisms that govern the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in living organisms.
From the intricate structures involved in gas exchange to the regulatory mechanisms that ensure efficient respiration, this activity offers a comprehensive understanding of this vital physiological process.
Gas Exchange Overview
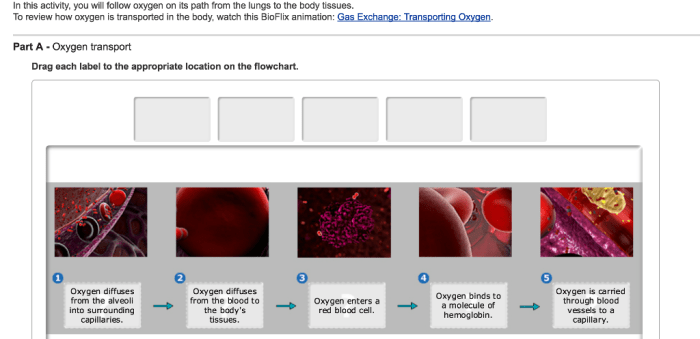
Gas exchange is the process by which living organisms exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide with their environment. In humans, this process occurs in the lungs, where oxygen from the air is taken into the bloodstream and carbon dioxide from the bloodstream is released into the air.
The process of gas exchange is divided into two phases: inhalation and exhalation.
Inhalation
Inhalation is the process of taking air into the lungs. It is an active process that requires the use of muscles to expand the chest cavity and draw air in through the nose and mouth. The air then travels down the trachea and into the lungs.
Exhalation
Exhalation is the process of releasing air from the lungs. It is a passive process that occurs when the muscles of the chest cavity relax and the lungs recoil. The air is then expelled through the nose and mouth.
Structures Involved in Gas Exchange
The key organs and structures involved in gas exchange are the lungs, trachea, and alveoli.
Lungs
The lungs are two large, spongy organs located in the chest cavity. They are made up of millions of tiny air sacs called alveoli.
Trachea
The trachea is a tube that connects the nose and mouth to the lungs. It is lined with cilia, which help to move mucus and foreign particles out of the lungs.
Alveoli
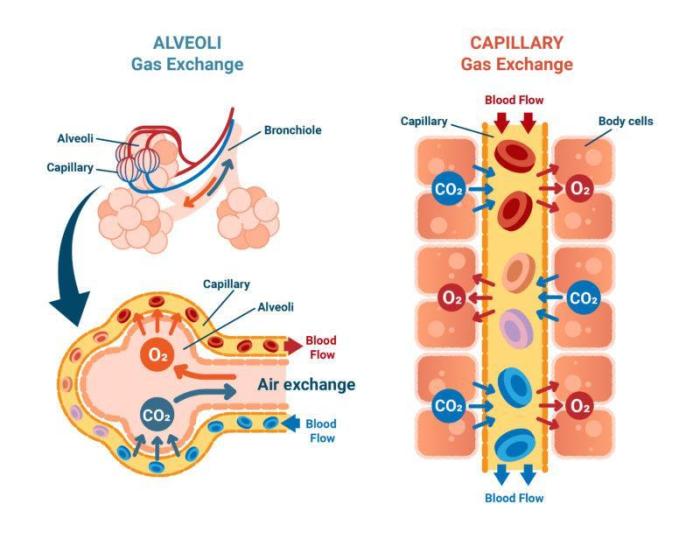
The alveoli are tiny air sacs in the lungs where gas exchange occurs. They are lined with capillaries, which are small blood vessels that allow oxygen and carbon dioxide to pass through.
Mechanisms of Gas Exchange
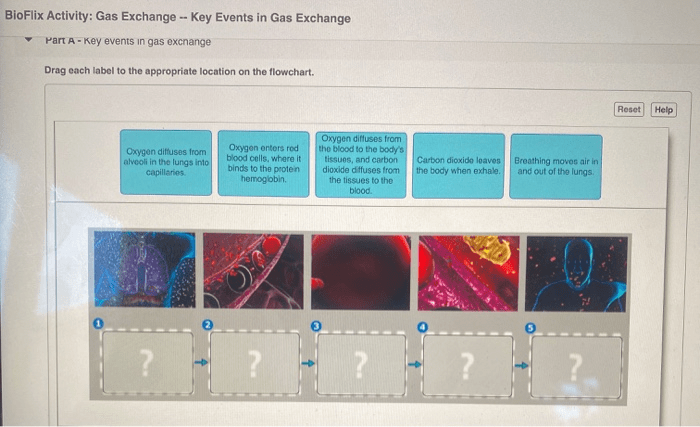
Gas exchange occurs by the process of diffusion. Diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. In the lungs, oxygen diffuses from the alveoli into the capillaries, and carbon dioxide diffuses from the capillaries into the alveoli.
The rate of diffusion is determined by the following factors:
- The concentration gradient of the gas
- The surface area of the exchange surface
- The thickness of the exchange surface
Regulation of Gas Exchange

The rate of gas exchange is regulated by the respiratory center in the brain. The respiratory center monitors the levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood and adjusts the rate of breathing accordingly.
The following factors can influence the rate of breathing:
- The level of physical activity
- The temperature of the environment
- The pH of the blood
Disorders of Gas Exchange: Bioflix Activity: Gas Exchange — Inhaling And Exhaling
There are a number of disorders that can affect gas exchange. These disorders can range from mild to severe and can be caused by a variety of factors.
Asthma
Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease of the airways. It can cause wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath.
Emphysema
Emphysema is a chronic lung disease that causes damage to the alveoli. This can lead to shortness of breath, fatigue, and weight loss.
Applications of Gas Exchange Principles
The principles of gas exchange are used in a variety of medical devices and therapies.
Artificial Respiration
Artificial respiration is a medical procedure that provides mechanical ventilation to a patient who is unable to breathe on their own.
Oxygen Therapy, Bioflix activity: gas exchange — inhaling and exhaling
Oxygen therapy is a medical treatment that provides supplemental oxygen to a patient who is not getting enough oxygen from the air.
Detailed FAQs
What is the primary function of the lungs in gas exchange?
The lungs serve as the primary site for gas exchange, facilitating the diffusion of oxygen into the bloodstream and the removal of carbon dioxide from the body.
How does the respiratory center in the brain regulate breathing?
The respiratory center monitors blood pH and carbon dioxide levels, adjusting breathing rate and depth to maintain optimal gas exchange.
What is the role of diffusion in gas exchange?
Diffusion is the passive movement of gases from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration, driving the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide across the respiratory surfaces.