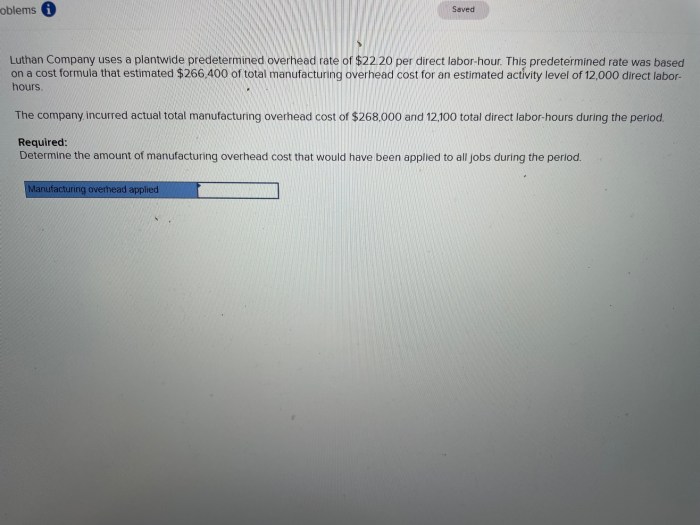
Luthan company uses a plantwide predetermined – Luthan Company’s utilization of a plantwide predetermined overhead rate presents a fascinating case study in cost accounting. This comprehensive analysis delves into the intricacies of this approach, exploring its advantages, disadvantages, and practical applications.
By employing a plantwide predetermined overhead rate, Luthan Company aims to distribute overhead costs equitably across all products and services. This approach simplifies the allocation process and enhances cost transparency. However, it also introduces certain limitations that must be carefully considered.
Plantwide Predetermined Overhead Rate

A plantwide predetermined overhead rate (POHR) is a single rate that is used to allocate overhead costs to all products or services produced by a company. It is calculated by dividing the total estimated overhead costs for a period by the total estimated activity base for that period.
The advantage of using a POHR is that it is simple to calculate and use. It is also relatively easy to understand, which can make it easier to communicate to employees and other stakeholders. However, a POHR can be inaccurate if the overhead costs are not evenly distributed across all products or services.
This can lead to some products or services being over-costed and others being under-costed.
Examples of companies that use a POHR include:
- Manufacturers
- Service companies
- Retailers
Calculating the Plantwide Predetermined Overhead Rate: Luthan Company Uses A Plantwide Predetermined

The steps involved in calculating a POHR are as follows:
- Identify the overhead costs that will be included in the calculation.
- Estimate the total amount of overhead costs for the period.
- Identify the activity base that will be used to allocate the overhead costs.
- Estimate the total amount of activity for the period.
- Divide the total estimated overhead costs by the total estimated activity to calculate the POHR.
The types of overhead costs that are included in the calculation of a POHR can vary depending on the company. However, some common types of overhead costs include:
- Indirect labor
- Utilities
- Rent
- Insurance
- Depreciation
The activity base that is used to allocate overhead costs can also vary depending on the company. However, some common activity bases include:
- Direct labor hours
- Machine hours
- Units produced
Using the Plantwide Predetermined Overhead Rate

Once the POHR has been calculated, it can be used to assign overhead costs to products or services. To do this, the POHR is multiplied by the actual amount of activity for the product or service.
For example, if a company has a POHR of $10 per direct labor hour and a product requires 10 direct labor hours to produce, then the overhead cost for that product would be $100.
It is important to note that the accuracy of the POHR is critical to the accuracy of the overhead costs that are assigned to products or services. If the POHR is inaccurate, then the overhead costs will be misallocated, which can lead to incorrect product or service costing.
There are a number of potential errors that can occur when using a POHR. These errors include:
- Inaccurate estimation of overhead costs
- Inaccurate estimation of activity
- Incorrect allocation of overhead costs
Alternatives to the Plantwide Predetermined Overhead Rate
There are a number of alternatives to using a POHR. These alternatives include:
- Activity-based costing (ABC)
- Departmental overhead rates
- Variable overhead rates
ABC is a more sophisticated method of allocating overhead costs than a POHR. ABC assigns overhead costs to products or services based on the activities that are required to produce them. This can result in a more accurate allocation of overhead costs, but it can also be more complex and time-consuming to implement.
Departmental overhead rates are calculated separately for each department in a company. This can be a more accurate method of allocating overhead costs than a POHR, but it can also be more complex and time-consuming to implement.
Variable overhead rates are calculated based on the level of activity. This can be a more accurate method of allocating overhead costs than a POHR, but it can also be more complex and time-consuming to implement.
The best alternative to a POHR for a particular company will depend on the company’s specific circumstances.
Helpful Answers
What is the primary advantage of using a plantwide predetermined overhead rate?
Simplicity and ease of calculation.
What is a potential disadvantage of using a plantwide predetermined overhead rate?
Inaccuracy in cost allocation due to variations in overhead consumption across products.
How does Luthan Company calculate its plantwide predetermined overhead rate?
By dividing total estimated overhead costs by the estimated total activity base (e.g., direct labor hours or machine hours).